1925
1925
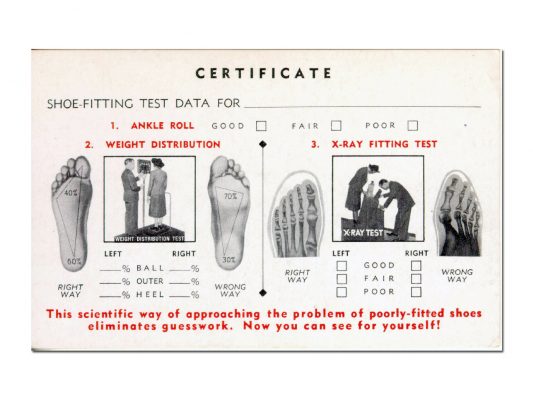
Radium water is beneficial
Radium was also used in drinking cups as a cure for at least 27 diseases. Water in the drinking cup had to stay there for at least 12 hours with the Radium source in it. A daily portion of this water would be very beneficial. The water was ionized and got a sparkling taste.
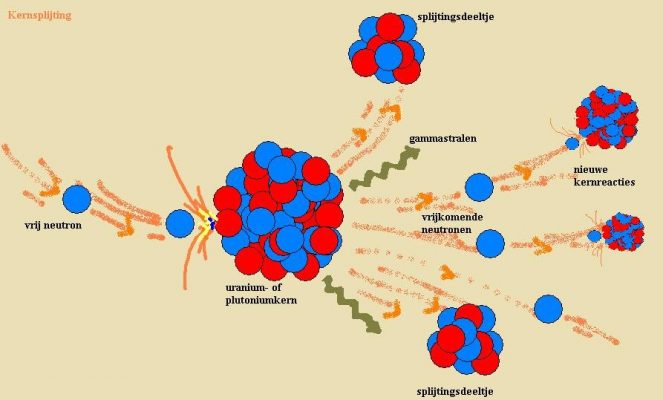 1938
1938
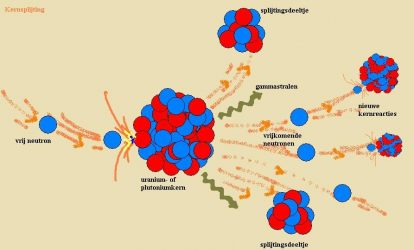
First nuclear fission
The fission process was discovered in 1938 by Otto Hahn and Fritz Strassmann in Berlin. Enrico Fermi and his associates were the first to bombard uranium with neutrons in 1934. The impetus for the discovery of nuclear fission was that a radioactive substance was formed that appeared to be chemically identical with barium, atomic number 56, which was thus considered impossible until then. With the help of directions from Meitner, the decisive experiment was conducted on December 17, 1938, and Hahn definitively determined that nuclear fission had taken place. The results were published in Die Naturwissenschaften in early 1939.
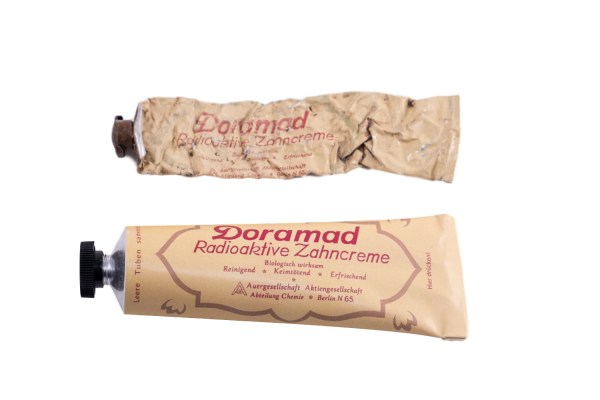 1940
1940
Radioactive toothpaste for German troops
Doramad Radioactive Toothpaste (Doramad Radioaktive Zahncreme) was a brand of toothpaste produced in Germany by Auergesellschaft of Berlin from the 1920s to World War II. The product was distributed to German troops before the First World War. The toothpaste was known for containing thorium, a radioactive metal, and is an example of radioactive quackery. This product is said to increase blood circulation in the gums, destroy germs, increase the life force in the tissues of the mouth and taste great.
 1941
1941
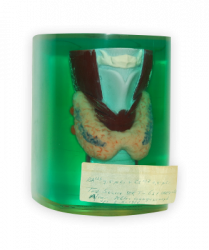
First use of radioactive iodine
In 1941 radioactive iodine was used for the first time in thyroid research. Radioactive iodine is used for testing the functioning of the thyroid gland. The thyroid gland produces hormones that are important for the regulation of the metabolism. For the production of these hormones, the thyroid gland is mainly dependent on iodine, which enters the body in small amounts with food. By measuring the uptake of radioactive iodine in the thyroid gland, an uptake that is too high or too low can be demonstrated.
 1945
1945
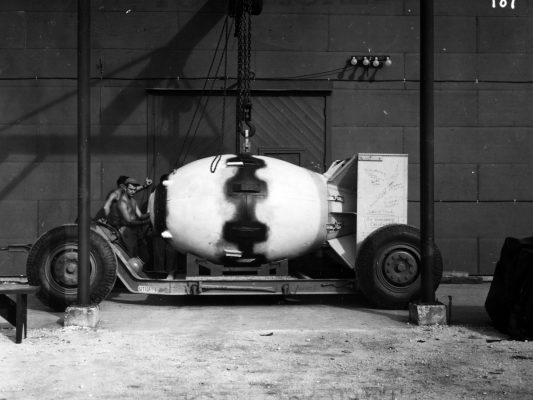
Atomic Bomb
The first ever atomic bomb, the Trinity Test, exploded in Alamogordo in the Nevada desert on July 16, 1945. The atomic bomb was the result of the Manhattan project.
On August 6, an atomic bomb containing 60 kilograms of enriched uranium detonated at 580 meters above Hiroshima. The bomb kills 130,000 people almost instantly and about 70,000 to 100,000 people in consequences afterward. Three days later, an atomic bomb containing plutonium detonated over Nagasaki.
 1950
1950
Coloring glaze with uranium
Long before uranium became known as a radioactive raw material for the generation of nuclear energy, it was mainly used as a means to color glass and glaze. The glass and glaze was relatively safe for the users due to the low concentration and confinement in the glass. It was less safe for the makers who had to deal with large quantities of powdered uranium.
 1953
1953
Atoms for peace
For the United Nations General Assembly, US President Eisenhower will deliver a speech that will go down in history as the ‘Atoms for Peace’ speech. Eisenhouwer announces that the US will give up its monopoly in nuclear technology. Nuclear technology should no longer be used to wage war, but serve humanity. He also calls for the creation of a control body to prevent countries with the technology from making nuclear weapons: this will lead to the establishment of the IAEA.
 1955
1955
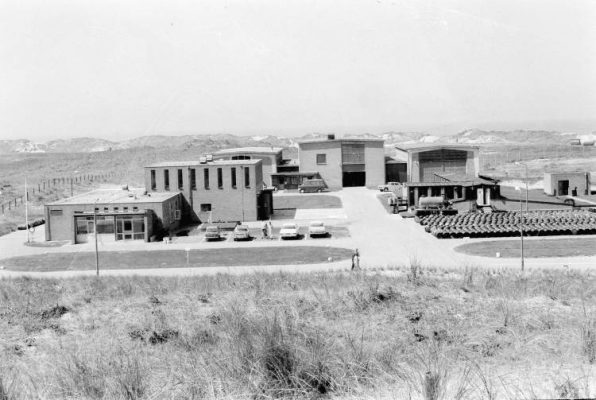
Start Reactor Center Netherlands
The current ECN (Energy Center Netherlands) started in 1955 as Reactor Center Netherlands. The aim of RCN was ‘to acquire knowledge about the peaceful application of nuclear energy and to make it available, in particular to Dutch institutions and companies’. RCN was founded by the Ministers of Education, Arts and Science and of Economic Affairs. The foundation had a large branch in Petten and a smaller one in Scheveningen. In addition to the low-flux reactor, a high-flux reactor was also commissioned in Petten in 1962.
 1957
1957
Founding of ITAL
On January 7, 1957, the Institute for the Application of Atomic Energy in Agriculture (ITAL) was established in The Hague with the aim of ‘promoting agriculture by stimulating, advising and conducting research on the application of ionizing rays and the use of isotopes and labeled compounds’. Wageningen was chosen as the location for ITAL; at the Agricultural College. A research reactor was also built on the ITAL complex.
 1957
1957
Het Atoom exhibition
In 1957 the exhibition Het Atoom was organized at Schiphol, where the miracle of atomic energy was explained. The exhibition broke visitor records almost daily. The showpiece was a working reactor purchased by the Department of Education, Arts and Science from AMF Atomics in New York.
 1957
1957
Establishment of the International Atomic Energy Agency
The International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) was founded in 1957 at the suggestion of US President Dwight D. Eisenhower, following his Atoms for Peace speech, on December 8, 1953, before the United Nations General Assembly, in which he advocated an international body to research and develop atomic energy. IAEA is an autonomous United Nations organization for scientific and technical cooperation in the field of nuclear technology and its peaceful uses.
 1958
1958
Hydrotector invented
The troxler contains a source that emits neutrons and a receiver that registers the reflected neutrons. When neutrons collide with hydrogen atoms, they enter a lower energy level. The number of neutrons with a lower energy level gives an indication of the amount of water in the subsoil. These devices are used in road construction and the roofing industry.
 1958
1958
Euratom Treaty in force
In 1957 the Euratom Treaty was signed in Rome. On January 1, 1958, the Euratom Treaty entered into force and the Euratom Commission was established in Brussels. The European Atomic Energy Community, Euratom for short, is an international organization with the aim of promoting peaceful uses of nuclear energy. Euratom is a separate organization, but for decisions it uses the institutions of the European Union. All countries that accede to the European Union must also accede to the Euratom Treaty.
 1961
1961
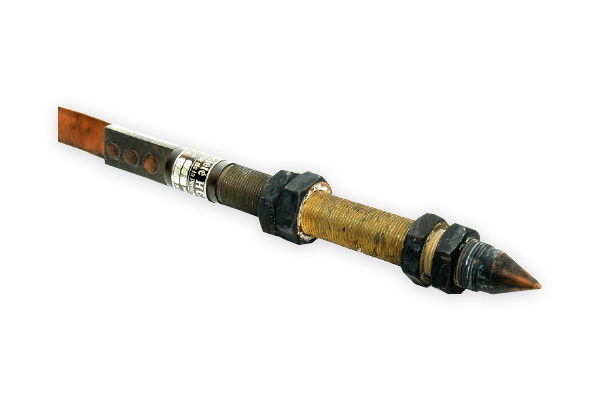
First technetium cow
In the middle of the container of the technetium cow is the radioactive substance molybdenum that is transported in this form to hospitals. The radioactive molybdenum decays to technetium. Technetium is a widely used radioactive substance for diagnosis. Because technetium has a short life, it is only removed from the “cow” in the hospital by means of elution (rinsing).
 1969
1969
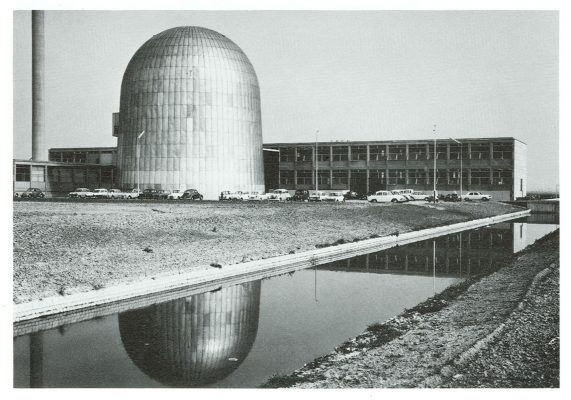
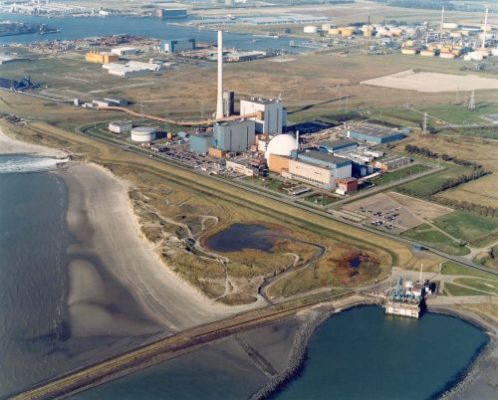
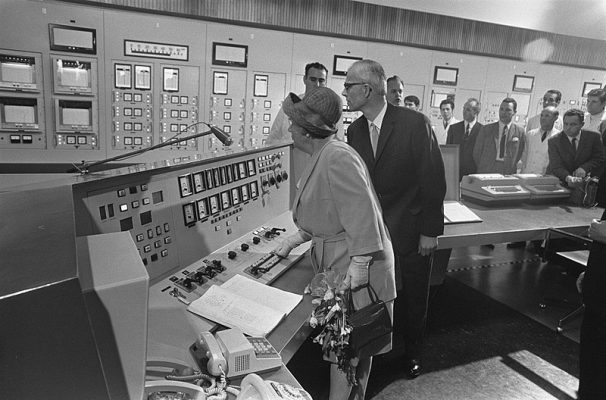
First nuclear power plant in the Netherlands
Dodewaard nuclear power plant was the first nuclear power plant in the Netherlands. NV Common Nuclear Power Plant Netherlands (GKN) was founded in 1965 as the owner and operator of the nuclear power plant. Construction began in 1965 and the nuclear reactor was commissioned in the presence of Queen Juliana on March 26, 1969. The plant was in operation until 1997.
 1982
1982
Establishment of COVRA
In 1982 the Central Organization for Radioactive Waste (COVRA) was founded with the task of collecting, processing and storing all radioactive waste in the Netherlands. In 1984 the first staff started working for COVRA and COVRA took over the collection of low and medium radioactive waste from ECN. COVRA still works from Petten.